Multinational Corporations (MNCs)
May 11, 2019(From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
A multinational corporation (MNC) or worldwide enterprise is a corporate organization which owns or controls production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country. Black’s Law Dictionary suggests that a company or group should be considered a multinational corporation if it derives 25% or more of its revenue from out-of-home-country operations. A multinational corporation can also be referred to as a multinational enterprise (MNE), a transnational enterprise (TNE), a transnational corporation (TNC), an international corporation, or a stateless corporation. There are subtle but real differences between these three labels, as well as multinational corporation and worldwide enterprise.

Most of the largest and most influential companies of the modern age are publicly traded multinational corporations, including Forbes Global 2000 companies. Multinational corporations are subject to criticisms for lacking ethical standards, and that this shows up in how they evade ethical laws and leverage their own business agenda with capital, and even the military backing of their own wealthy host nation-states. They have also become associated with multinational tax havens and base erosion and profit shifting tax avoidance activities.
A multinational corporation (MNC) is usually a large corporation incorporated in one country which produces or sells goods or services in various countries. The two main characteristics of MNCs are their large size and the fact that their worldwide activities are centrally controlled by the parent companies.
- Importing and exporting goods and services
- Making significant investments in a foreign country
- Buying and selling licenses in foreign markets
- Engaging in contract manufacturing — permitting a local manufacturer in a foreign country to produce their products
- Opening manufacturing facilities or assembly operations in foreign countries
MNCs may gain from their global presence in a variety of ways. First of all, MNCs can benefit from the economy of scale by spreading R&D expenditures and advertising costs over their global sales, pooling global purchasing power over suppliers, and utilizing their technological and managerial know-how globally with minimal additional costs. Furthermore, MNCs can use their global presence to take advantage of underpriced labor services available in certain developing countries, and gain access to special R&D capabilities residing in advanced foreign countries.
The problem of moral and legal constraints upon the behavior of multinational corporations, given that they are effectively “stateless” actors, is one of several urgent global socioeconomic problems that emerged during the late twentieth century.
Potentially, the best concept for analyzing society’s governance limitations over modern corporations is the concept of “stateless corporations”. Coined at least as early as 1991 in Business Week, the conception was theoretically clarified in 1993: that an empirical strategy for defining a stateless corporation is with analytical tools at the intersection between demographic analysis and transportation research. This intersection is known as logistics management, and it describes the importance of rapidly increasing global mobility of resources. In a long history of analysis of multinational corporations we are some quarter century into an era of stateless corporations – corporations which meet the realities of the needs of source materials on a worldwide basis and to produce and customize products for individual countries.
One of the first multinational business organizations, the East India Company, was established in 1601. After the East India Company, came the Dutch East India Company, founded March 20, 1603, which would become the largest company in the world for nearly 200 years.
The main characteristics of multinational companies are:
- In general, there is a national strength of large companies as the main body, in the way of foreign direct investment or acquire local enterprises, established subsidiaries or branches in many countries;
- It usually has a complete decision-making system and the highest decision-making centre, each subsidiary or branch has its own decision-making body, according to their different features and operations to make decisions, but its decision must be subordinated to the highest decision-making centre;
- MNCs seek markets in worldwide and rational production layout, professional fixed-point production, fixed-point sales products, in order to achieve maximum profit;
- Due to strong economic and technical strength, with fast information transmission, as well as funding for rapid cross-border transfers, the multinational has stronger competitiveness in the world;
- Many large multinational companies have varying degrees of monopoly in some area, due to economic and technical strength or production advantages.
Theoretical background
The actions of multinational corporations are strongly supported by economic liberalism and free market system in a globalized international society. According to the economic realist view, individuals act in rational ways to maximize their self-interest and therefore, when individuals act rationally, markets are created and they function best in free market system where there is little government interference. As a result, international wealth is maximized with free exchange of goods and services.
To many economic liberals, multinational corporations are the vanguard of the liberal order. They are the embodiment par excellence of the liberal ideal of an interdependent world economy. They have taken the integration of national economies beyond trade and money to the internationalization of production. For the first time in history, production, marketing, and investment are being organized on a global scale rather than in terms of isolated national economies.
International business is also a specialist field of academic research. Economic theories of the multinational corporation include internalization theory and the eclectic paradigm. The latter is also known as the OLI framework.
The other theoretical dimension of the role of multinational corporations concerns the relationship between the globalization of economic engagement and the culture of national and local responses. This has a history of self-conscious cultural management going back at least to the 60s. For example:
Ernest Dichter, architect, of Exxon’s international campaign, writing in the Harvard Business Review in 1963, was fully aware that the means to overcoming cultural resistance depended on an “understanding” of the countries in which a corporation operated. He observed that companies with “foresight to capitalize on international opportunities” must recognize that “cultural anthropology will be an important tool for competitive marketing”. However, the projected outcome of this was not the assimilation of international firms into national cultures, but the creation of a “world customer”. The idea of a global corporate village entailed the management and reconstitution of parochial attachments to one’s nation. It involved not a denial of the naturalness of national attachments, but an internationalization of the way a nation defines itself.
Transnational corporations
A transnational corporation differs from a traditional multinational corporation in that it does not identify itself with one national home. While traditional multinational corporations are national companies with foreign subsidiaries, transnational corporations spread out their operations in many countries to sustain high levels of local responsiveness.
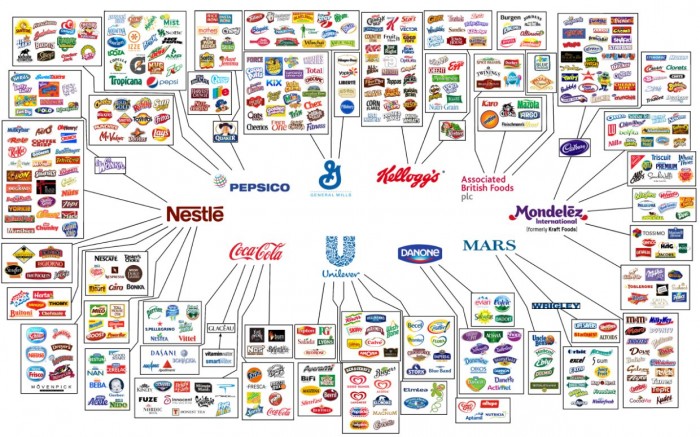
An example of a transnational corporation is Nestlé, who employ senior executives from many countries and tries to make decisions from a global perspective rather than from one centralized headquarters.
Another example is Royal Dutch Shell, whose headquarters are in The Hague, Netherlands, but whose registered office and main executive body are headquartered in London, United Kingdom.
Multinational enterprise
“Multinational enterprise” (MNE) is the term used by international economist and similarly defined with the multinational corporation (MNC) as an enterprise that controls and manages production establishments, known as plants located in at least two countries. The multinational enterprise (MNE) will engage in foreign direct investment (FDI) as the firm makes direct investments in host country plants for equity ownership and managerial control to avoid some transaction costs.
Colonialism
The history of multinational corporations is closely intertwined with the history of colonialism, the first multinational corporations being founded to undertake colonial expeditions at the behest of their European monarchical patrons. Prior to the era of New Imperialism, a majority European colonies not held by the Spanish and Portuguese crowns were administered by chartered multinational corporations. Examples of such corporations include the British East India Company, the Swedish Africa Company, and the Hudson’s Bay Company. These early corporations facilitated colonialism by engaging in international trade and exploration, and creating colonial trading posts. Many of these corporations, such as the South Australia Company and the Virginia Company, played a direct role in formal colonization by creating and maintaining settler colonies. Without exception these early corporations created differential economic outcomes between their home country and their colonies via a process of exploiting colonial resources and labour, and investing the resultant profits and net gain in the home country. The end result of this process was the enrichment of the colonizer and the impoverishment of the colonized. Some multinational corporations, such as the Royal African Company, were also responsible for the logistical component of the Atlantic slave trade, maintaining the ships and ports required for this vast enterprise. During the 19th century, formal corporate rule over colonial holdings largely gave way to state-controlled colonies, however corporate control over colonial economic affairs persisted in a majority of colonies.
During the process of decolonization, the European colonial charter companies were disbanded, with the final colonial corporation, the Mozambique Company, dissolving in 1972. However the economic impact of corporate colonial exploitation has proved to be lasting and far reaching, with some commentators asserting that this impact is among the chief causes of contemporary global income inequality.
Contemporary critics of multinational corporations have charged that some present day multinational corporations follow the pattern of exploitation and differential wealth distribution established by the now defunct colonial charter corporations, particularly with regards to corporations based in the developed world that operate resource extraction enterprises in the developing world, such as Royal Dutch Shell, and Barrick Gold. Some of these critics argue that the operations of multinational corporations in the developing world take place within the broader context of neocolonialism.
However, multinational corporations from emerging markets are playing an ever-greater role, increasingly impacting the global economy.
Criticism
Anti-corporate advocates criticize multinational corporations for being without a basis in a national ethos, being ultimately without a specific nationhood, and that this lack of an ethos appears in their ways of operating as they enter into contracts with countries that have low human rights or environmental standards. In the world economy facilitated by multinational corporations, capital will increasingly be able to play workers, communities, and nations off against one another as they demand tax, regulation and wage concessions while threatening to move. In other words, increased mobility of multinational corporations benefit capital while workers and communities lose. Some negative outcomes generated by multinational corporations include increased inequality, unemployment, and wage stagnation.
The aggressive use of tax avoidance schemes, and multinational tax havens, allows multinational corporations to gain competitive advantages over small and medium-sized enterprises. Organizations such as the Tax Justice Network criticize governments for allowing multinational organizations to escape tax, particularly by using base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) tax tools, since less money can be spent for public services.